BI Areas
Data Sourcing
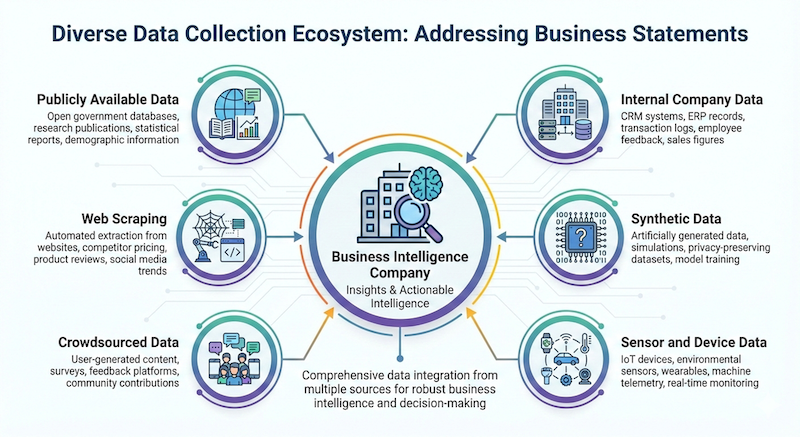
Sourcing of right data to address a business statement is one of the foundations of our entire business intelligence approach. There are many data collection points to address an business statement – publicly available data set, internal company data, web scraping, synthetic data, crowdsourced data, sensor and device data.
With the diversity of the content, formats and locations, the data to be handled is immense. We identify the right data sources, business goal as well as the data to make them work in tandem to arrive at knowledge for better decision making.
Business Logic
Data collection through various sources needs to be cleaned, calculations to be applied, structured and converted into standardised formats before being stored. This allows organisations to have single definition, or a uniform data processing across. Some of the attributes need special attention as they may be in different formats. Also, the varied data sources need to be homogenised. This is where data is converted to information. Data exceptions and data quality are also addressed here.
Business strategies and roadmaps keep changing and hence the model we develop is agile, modifiable and scalable. We are always on a lookout for new parameters that can affect the business, create business function specific logics, remove data inconsistency, watch out for data compliance and regulatory requirements.
After the data is collected and transformed, it is stored in data warehouses keeping in mind the viable structures and business function specific data marts. Data storage can depend upon organisation’s requirements and can be through traditional on premise servers, cloud or hybrid models.
Reporting
A rich graphic interface helps users to consume large amounts of information and draw insights at a glance. These visual reports are designed with the twin objective of understandability and performance in mind. Visualisations includes representing data with colours, brightness, size, shape, graphs, maps, motion of visual objects representing aspects of data being analysed.
There are different types of analysis and reporting depending upon the type of question you want answered.
Example, a dashboard for monthly progress report will answer broader questions about the strategy whereas daily report will give insights into sales efforts. There can be custom and ad hoc reports for targeted questions like no of units sold of a particular product every day of the week.
Long gone are the days when you actually needed an IT team to source and process data every time. Nowadays, enterprise reporting in business intelligence allows viewing of data with dynamic filters, drill downs, excluding outliers, and dynamic calculations. Also, depending on the size of organisation as well as business models, visualisations are used for business’s advantage.

Analytics
Analytical tools transform or digest the output from data warehouses to draw insights, provide prescriptive analysis and advanced predictive analysis. The whole objective of analytics is to support data driven decision making.
In an organisation, fact based decision making is encouraged and rewarded. Traditionally, data was keyed into spreadsheets, documents were earmarked with post its and markers. However, with our BI infrastructure we make analysis easy and automated.
Decision making these days is dynamic, managers need on demand access to decision making business tools and applications. With BI implementation, business users can have access to interactive style of insights from advanced analytics without requiring them to have technical or data science skills.

Other BI Needs
Business Intelligence needs of an organisation can be varied. It becomes very difficult to encapsulate all what an organisation wants under certain heads. Other organisational needs may include enabling the organisation with the right skillset and right people to maintain as well as effectively run the business intelligence eco-system.
Modern day business intelligence platforms are hosted on cloud and are collaborative in nature. They allow people to collaborate on various reports, access data and information using any device and from anywhere they are. Notifications and alerts allow for real time distribution of metrics via email or messaging systems.

